-
Learn more about...
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Personality: TAI
- Temperament
- Ability
- Interests
- Recent Blog Posts
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator® (MBTI®)
- Creativity
- Parsimony in Personality
- Code Sharing: scienceCareers
- Presidential Candidacy and Personality
- Eysenck Personality Questionnaire® (EPQ)
- The HEXACO Model
- The RIASEC Model
- The CHC Model
- The NEO-PI-R
- see more...
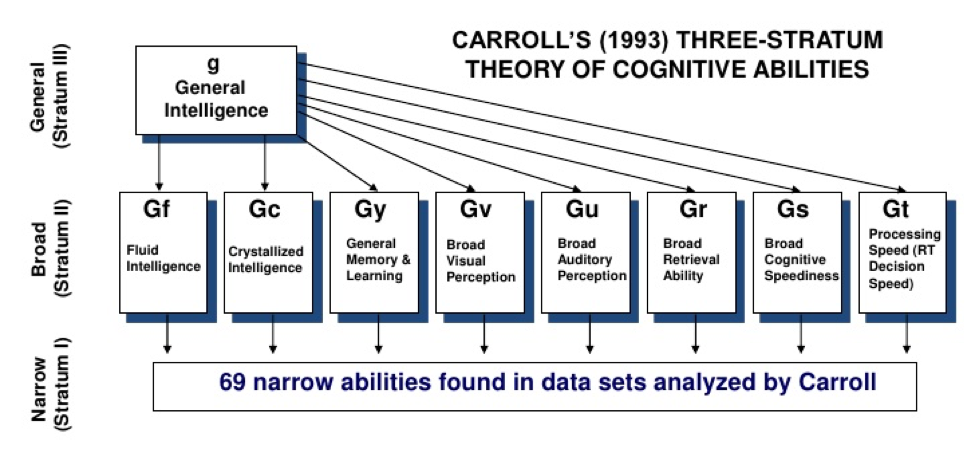
The Cattell-Horn-Carroll (CHC) model of intelligence is perhaps best explained by breaking the theory down into parts that loosely correspond to the researchers after which it was named – Raymond Cattell, John Horn, and John Carroll. In the early 1940s, Cattell began developing his two factor, Gf-Gc, model of intelligence. “Gf” is the notation for fluid intelligence which can be broadly defined as one’s ability to use logic in a new situation and solve new problems with deductive or inductive reasoning, while “Gc” refers to crystallized intelligence which consists mostly of knowledge and abilities acquired over time.
Beginning in the 1960s and continuing well into the 1990s, John Horn built upon Cattell’s work. Eventually, together, they proposed an eight factor model of intelligence which included measures of short-term memory, reading/writing ability, quantitative ability, and decision speed (to name a few). A new, revised structure of cognitive ability came from Carroll’s work during the 1990s. He proposed three strata or levels of abilities – general, broad, and narrow (see figure). When Horn and Carroll both attended a meeting regarding the Woodcock-Johnson tests of cognitive abilities, the similarities in their theories were quickly recognized.
The most recent version of CHC theory includes 10 broad cognitive abilities and over 70 narrow abilities. Before 1998, the majority of intelligence battery tests measured only a few of the broad cognitive abilities. However, measures grounded in the CHC approach provide a way for practitioners and researchers to assess a much wider range of abilities than prior intelligence batteries. In a review of the influence of CHC theory on intelligence testing, Alfonso and colleagues
References:
[1] Alfonso, V. C., Flanagan, D. P., & Radwan, S. (2005). The impact of the Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory on test development and interpretation of cognitive and academic abilities.
[2] Cattell, R. B. (1957).
[4] Willis, J. O., Dumont, R., & Kaufman, A. S. (2011). Factor-analytic models of intelligence.